Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is a talking therapy that uses techniques to change how we think and behave in difficult situations. Breaking down the name can help it become less intimidating.
– Cognitive therapy: Focusing on the things you think
– Behaviour therapy: Focusing on the things you do
Throughout the treatment, you will work collaboratively with a therapist to recognise, challenge, and change negative thought patterns and behaviour patterns that are causing and maintaining distress.
What is it based on?
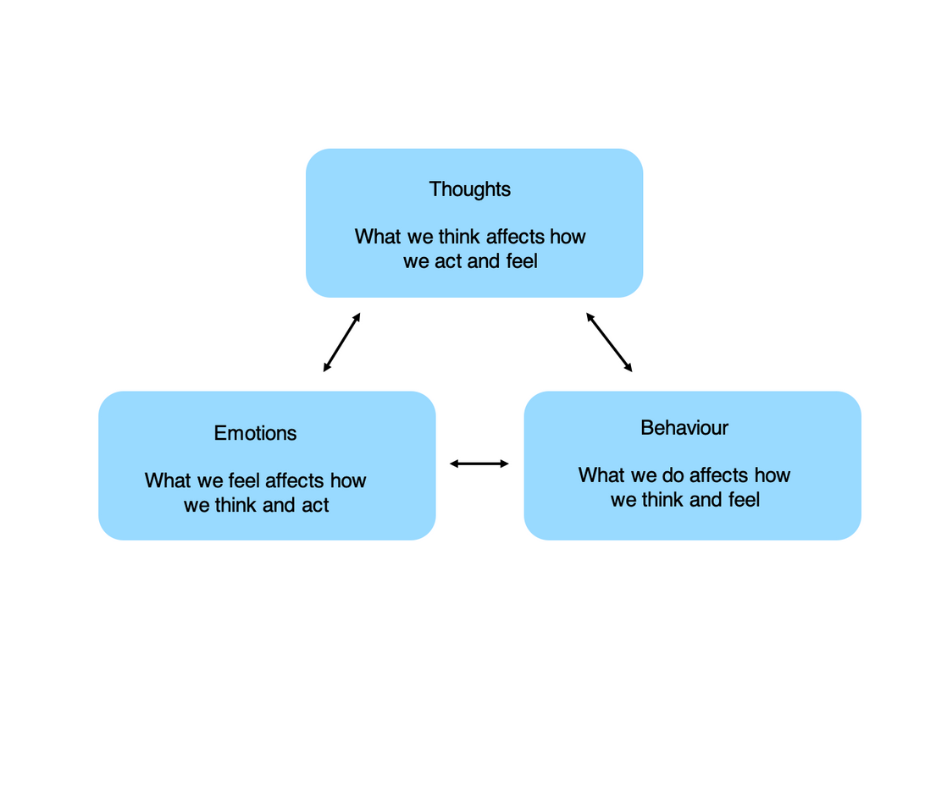
The theory behind CBT is that all our thoughts, feelings and actions are interconnected. Over time we pick up habits and negative thoughts that feed this cycle until it grows, sometimes feeling like it is out of control. However, we are never broken, just stuck and CBT aims to help break vicious cycles. It does this by challenging automatic habits and shifting your outlook on life into something more positive and healthier.
What can I expect from CBT?
A typical CBT session will focus on any problems that are affecting you right now. Past experiences may be relevant, but CBT is usually focused on the present and looking towards the future.
CBT tends to be a relatively short-term treatment. You and your therapist will decide on the duration and frequency of your sessions. During the sessions, you will work with your therapist through different exercises. These will explore the links between your thoughts, feelings, and behaviours relevant to your situation.
Outside the sessions, tasks will be set for you to complete and bring back to the session. This might include filling out a worksheet or keeping a diary. It could also be helpful a resource to refer back to once the treatment has finished.
What can CBT help with?
CBT is an effective way to treat several different mental health conditions. Below are a few examples:
– Eating disorders
– Phobias
– Sleeping problems
– Borderline personality disorder
– Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
– Alcohol misuse
– Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Individuals with long-term health conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), chronic / persistent pain, fibromyalgia or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) also benefit from CBT. Although CBT cannot cure physical symptoms, it has helped people learn to cope with them and lessen the effect on their daily life.
Is CBT effective?
CBT can be a very effective form of therapy for a lot of people. It is has strong evidence base, which means it is proven by research. It is recommended by the NHS and National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE). It is used internationally and by people in a range of situations.
Of course, sometimes it does not work as well or as quickly as we might like. It might just not be the best option for you and your situation, it might not be the right time in your life or you may need time to practice the techniques learnt during the sessions, and find what works for you.
North East Psychology offer CBT. If you would like to find out more use our contact us page, call 07870 241970 or email hello@nepsychology.co.uk.


